Atopic Dermatitis Profile
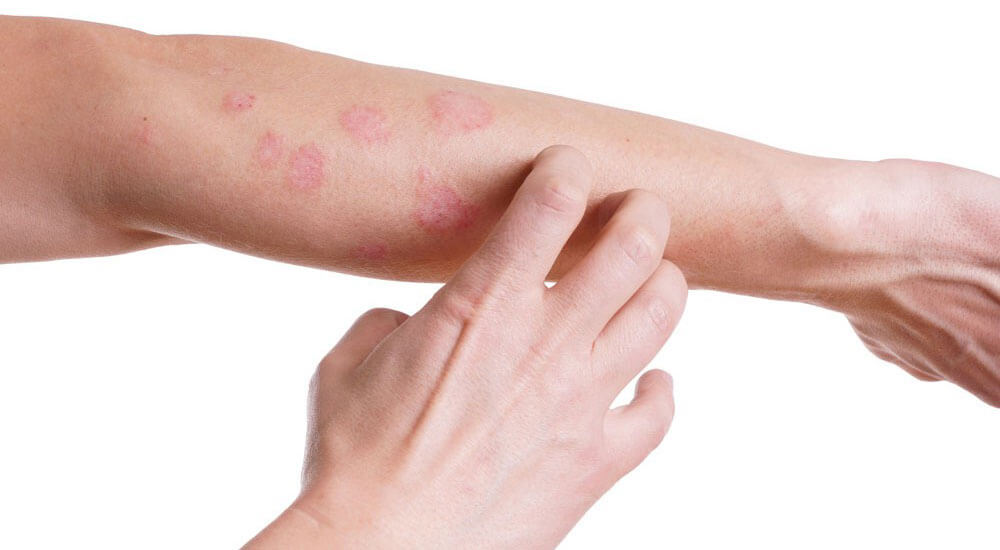
Atopic dermatitis is one of the most frequent skin disorder at an early or teenage age. But a lot of adults cannot treat it for many years. Statistics shows that 4 out of 5 children at preschool age have symptoms of this disorder, although atopic dermatitis becomes chronic not for all patients. Atopic dermatitis belongs to the so-called heterogenous group of dermatologic diseases – allergodermathoses the development of which is mainly provoked by allergic reactions of prolonged and instant type, but not only these ones.
The second group along with atopic dermatitis includes:
- Urticarial fever;
- Allergic dermatitis;
- Eczema;
- Toxicodermitis.
It is noteworthy that increased psycho-emotional and intellectual stress (stressful conditions), incorrect dietary regimen, sleep and wakeful state, polluted air are also provoking factors for development of atopic dermatitis, especially at an early age.
Causes and Mechanism of Atopic Dermatitis Development
Considerable tole in atopic dermatitis occurrence belongs to inheritance, since research studies discovered the following connection:
- If both parents healthy, possibility of this disease development is 20%;
- If one of parents had or has acute or chronic dermatitis form, risk is equal to 50%;
- In case both parents suffered or suffer from this disorder, probability of its development in a child is close to 80%.
Thus, atopic dermatitis (alias AD, atopic eczema, or constitutional eczema) is called by dermatologists a hereditary chronic allergic dermatosis with relapsing progression manifested with paroxysmal itch, erythematous papular rash, gradual appearance of skin lichenification.
Lichenification means induration of skin covering and enhancement of its pattern in paces of increased chronic irritation and rash.
Dermatologists distinguish three stages of atopic dermatitis development:
- Early – from 2 months to 3 years;
- Pediatric – 4-7 years;
- Mature from 8 years and older.
Although clinical presentation at these age groups differs a bit, constant symptom remains the same – paroxysmal itch. Generally, in case atopic dermatitis was not cured at puberty age, it accompanies a man throughout life in mild, moderate and severe forms with periodic relapses. As a medical term, atopy is translated from Latin as queerness or anomalousness and was first introduced by the doctor, A.F.Coca, in the first half of 20th century for collective naming of various hereditary versions of human hypersensitivity and forming in blood of antibodies to different allergens types. Its application is not accidental, since in majority of cases, an authentic cause of atopic dermatitis cannot be identified. According to large scale studies of the mid of 20th century, atopies (which include bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis and many other diseases apart from atopic dermatitis) affected not less than 10 per cent of planet’s population (today this figure is likely to be bigger). Moreover, it was stated that atopies often cause imposition of one atopic symptoms on the others.
Mechanisms of atopy progression are explained by conformity of instant-type allergic reactions production by organism which include succession of immune-nosochemic-nosophysiologic alterations. What does it mean?
Immunologic stage is accompanied with development of skin-sensitizing antibodies (cytophilic antibodies) which are exposed easily by means of laboratory method – Prausnitz-Kustner reaction.
Blood saturation with antibodies (cytophilic antibodies) corresponds to dermatologic sensibilization (enhanced reactive sensitivity of cells and tissues), but it is not always proportional to the level of clinical sensitivity or symptom load. When antibodies get attached to allergens on intracellular level, alteration of cellular structures occurs (their damage with extraneous agents) – biologically active elements are released from cells which leads to transmission to nosochemic stage of atopy development.
Tissue-effector, in turn, reacts on released biologically active substances and complex “allergen- cytophilic antibody” which is manifested by occurrence of nosophysical alterations of skin covering: vascular penetration increases, tissues swell, hypersecretion of tissues and contraction of smooth muscle cells (vascular walls) may occur.
Structural alterations in skin tissue is similar to external symptoms of anaphylaxis (vulnerability and sensitivity of immunity). They include edema, infiltration with eosinophils and histiocytes, and fibrinoid collagen disorganization. Moreover, anaphylaxis is usually induced by proteins, whereas atopy is suddenly developed hereditary hypersensitivity not only to protein substances, but also to compositions of non-proteinous origin.
Predisposition to atopic dermatitis is supposed to be transmitted by means of a couple of allerges of “H” and “h” type.
Symptoms and Diagnostics of Atopic Dermatitis
Besides the afore-described clinical picture of atopic dermatitis, this disease may be accompanied by functional disorders of central and vegetative nervous system:
- Anxiodepressive conditions and accentuated traits of character;
- Cortex neurodynamics with prevailing sympathoadrenal focus of initial vegetative tonus (indicators in relaxed wake state) and vegetative reactivity (response on inner and external stimuli) of cardiovascular system;
- Impairment of lymphocyte beta-adrenergic receptors functionality;
There are also dysfunctions of gastro-intestinal tract:
- Dysbiosis (dysbacteriosis);
- Enzymatic disease;
- Dyskinesia (suddenly occurred involuntary movements in various muscular groups);
- Malabsorption syndrome (impaired intestinal absorption);
- Impairment of kallikrein-kininogenin system, a group of high molecular weight proteins, polypeptides and enzymes directly influencing inflammatory processes in organism lead to enlargement of vascular permeability of skin, decrease of blood clotting ability, impairment of neuro-receptor apparatus functioning.
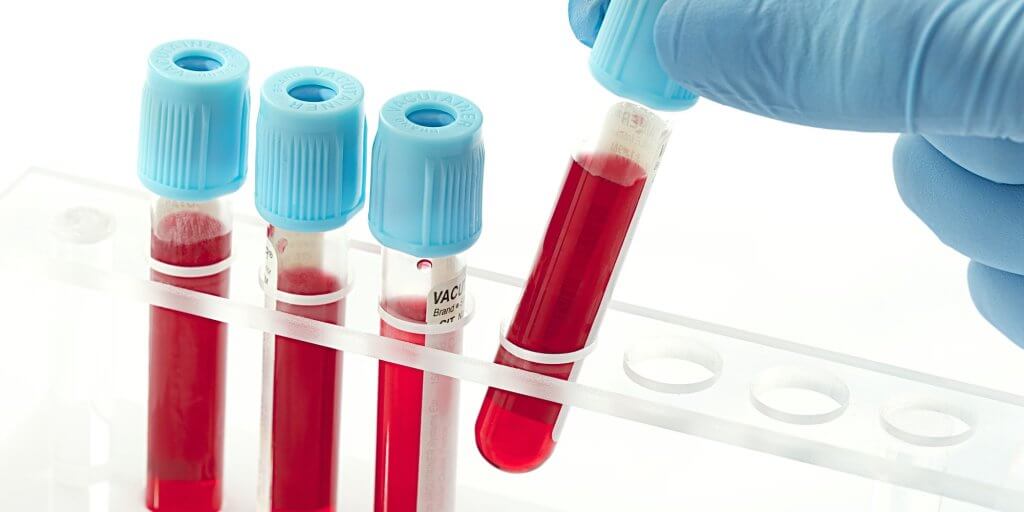
The described clinical picture and symptomatology allow making preliminary diagnosis of this disease, but in order to make a final diagnosis, laboratory diagnostics is required:
- Detection of allergens by means of skin scarifying (via scratch), intracutaneous and provocative tests (via nasal and ocular mucosa);
- Blood tests – complete blood cell count, eosinophilia test, immunogram, proteinogram, analysis for all types of allergens detection (alimentary, mite-borne, fungal, pollinic and others), for determination of hormonal profile, for glycemic and glycosuric profile, for antibodies to parasites.
- Clinical urine examination.
- Feces analysis – bacteriological analysis for dysbacteriosis, helminthosis, coprogram of physical, chemical and microscopic characteristics of feces.
Diagnosis is based on both: clinical picture and data of familial history (history of family members’ diseases), as well as on the results of laboratory and instrumental examination of a patient.
Histological studies in case of atopic dermatitis uncover the following conditions pronounced on epidermis:
- Acanthosis (pigmentation of skin folds area);
- Parakeratosis (impairment of the process of epidermis cells keratinization);
- Hyperkeratosis (scaliness of skin);
- Mild spongiosis (intercellular edema).
In skin covering vasodilation of capillaries occurs; around vessels of corpus papillare are infiltrates of lymphocytes.
Atopic Dermatitis Therapy by Canadian Health&Care Mall Rx
As a rule, every patient of dermatologist suffering from atopic dermatitis is assigned a strictly individual and grounded complex therapy:
- Hypoallergic diet and treatment-and-prophylactic regimen;
- External and systemic medicamentous therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Psychotherapy;
- Balneotherapy;
- In the most severe cases – surgery.
Hypoallergic diet and treatment-and-prophylactic regimen
Treatment-and-prophylactic regimen includes hygiene matters, washing, particular outfit wearing, sleep regulation, strolls in the open air, as well non-specific excluding diet.
External and systemic medicamentous therapy
If taken into account that atopic dermatitis occurrence involves a lot of etiological and pathogenetic factors, either local or systemic medicamentous therapy of the whole spectrum of modern clinical medicine is applied, such as:
- Antimicrobial agents;
- Cytostatic agents (anticancer drugs) and non-specific anti-inflammatory medications;
- Antihistamines of the second and third generations;
- Membrane stabilizers and anti-mediator agents;
- Medicines influencing central and vegetative nervous system: psychotropic and desensitizing drugs;
- Quinolines and anti-mycotic groups of azoles, allylamines and polyenes;
- Immunocorrectors, adaptogens, and biogenic stimulators in accordance with immunogram indexes;
- Gastrointestinal adsorbents and plasmapheresis;
- Components improving intestinal microflora;
- Vitamins, micro- and macroelements, anabolic agents;
- Polyvitaminic complexes with micro- and microelements and anabolics
Psychotherapy
Due to the fact that aggravation of atopic dermatitis generally starts after negative psychic impacts, a number of AD cases lead to repetitive neuroses and psychoses; therefore, importance of psychotherapy cannot be underestimated. A psychotherapist may apply such methods as electrical sleep, hypnosis, heterosuggestion and medicamentous therapy.
Physiotherapy
Therapy practice of atopic dermatitis shows high efficiency of various modern methods of physiotherapy. Moreover, in majority of cases it is essential. The range of physiotherapeutic methods includes impact on affected areas with cold, warmth, electrical current, ultraviolet, ultrasound, magnet, oxygen and ozone, as well as combination of physical and chemical impacts, such as phonophoresis and photochemotherapy. It goes without saying that all methods have their indications and contraindications which should be taken into account in case of physiotherapeutic procedures prescription.
Balneotherapy
In case of chronic dermatologic diseases of neurogenic, allergic or metabolic character, practically all physicians recommend conducting balneotherapy from time to time. Anyway, it should be conducted exclusively during relapse period.
Canadian Health&Care Mall Rx Professionals – canadianhealthcaremallrx.com



